Tracking red-cockaded woodpeckers through winter and their recovery
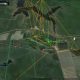
Grace Remains in North Carolina 1/29/2016
February 1, 2016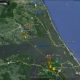
Grace Flies to Virginia Beach Feb 7 2016
February 8, 2016
This winter marked the Center’s 12th year of conducting the annual winter survey of the red-cockaded woodpecker population at the Nature Conservancy’s Piney Grove Preserve. We monitor the population of red-cockaded woodpeckers by conducting a full census of all individuals in the spring just before the breeding season and again during the winter. We also monitor all nesting activity in the early summer. Because every bird in the population is color banded as nestlings, we can follow the movement of individuals between breeding groups, assess their survival, and determine their breeding behavior. The winter survey provides an opportunity to examine how the autumn-winter period influences survival patterns and document the dispersal of adults and summer fledglings.
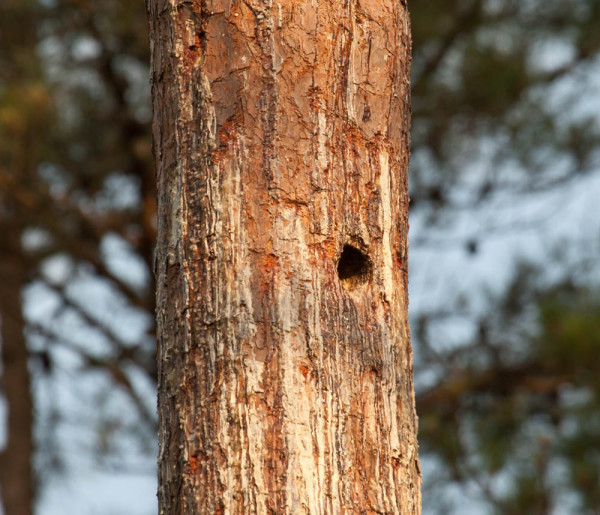

Red-cockaded woodpecker (RCW) cavity moments after a bird exited during the morning survey. RCWs drill resin wells around cavity entrances to deter predators with the flowing sap. Photo by Bryan Watts.
During the winter of 2015-2016, we recorded the highest number of red-cockaded woodpeckers in decades with 69 individuals distributed among 14 groups. Red-cockaded woodpeckers are cooperative breeders so groups may contain the breeding male and female, as well as additional birds that assist with incubating and feeding young. These groups will remain together throughout the entire annual cycle and travel together daily for foraging even in winter. The Piney Grove population continues to grow every season as the winter survey has shown through time with 29 birds detected in 2002, 45 birds in 2011, and 57 birds as recent as 2013. Among the birds detected this past survey included 16 of the 21 birds fledged in 2015. We typically lose 50-75% of the recently fledged birds by winter so the number of birds remaining bodes well for new recruitment into the 2016 breeding population.
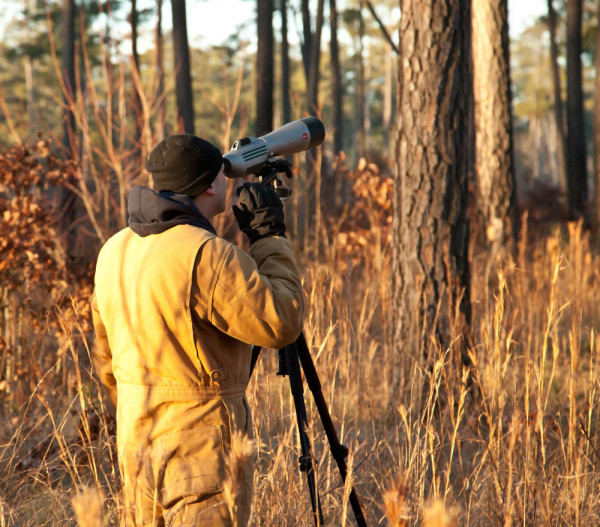

Mike Wilson surveys red-cockaded woodpeckers at the Piney Grove Preserve. Photo by Bryan Watts.
The Nature Conservancy’s Piney Grove Preserve has been the nucleus of recovery in the state since the early 2000s when the Commonwealth’s population of woodpeckers sank to an all-time low. A multi-organizational partnership that includes the Nature Conservancy, The Center for Conservation Biology, the Virginia Department of Game and Inland Fisheries, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, has worked together on habitat and population management to bring the number of red-cockaded woodpeckers back from the brink.
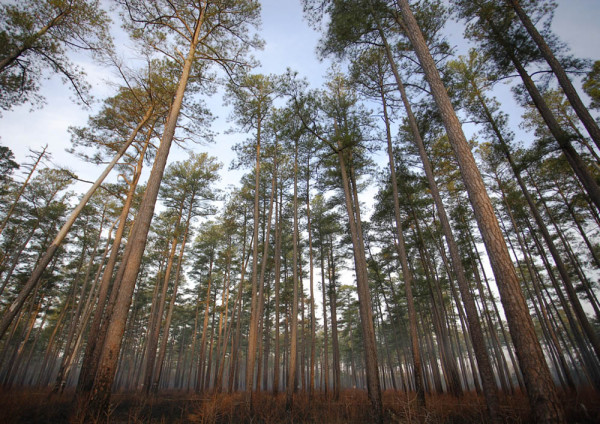

The Piney Grove Preserve at early morning. The old-growth pine preserve is maintained as ideal habitat for red-cockaded woodpeckers with prescribed fire to maintain an open, low understory. Photo by Bart Paxton.
Written by Mike Wilson | mdwils@wm.edu | (757) 221-1649
February 4, 2016
